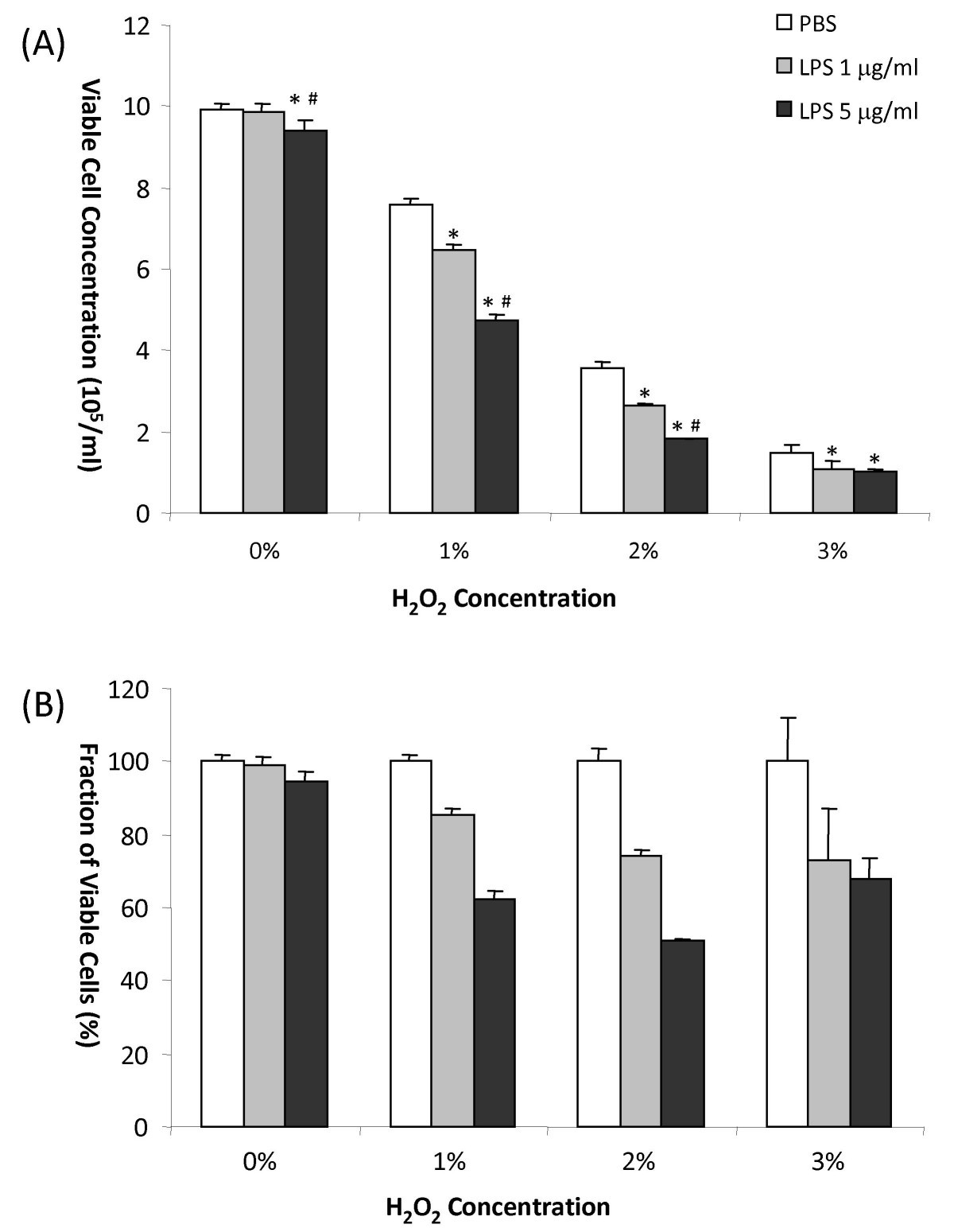
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) potentiates hydrogen peroxide toxicity in T98G astrocytoma cells by suppression of anti-oxidative and growth factor gene expression | BMC Genomics | Full Text

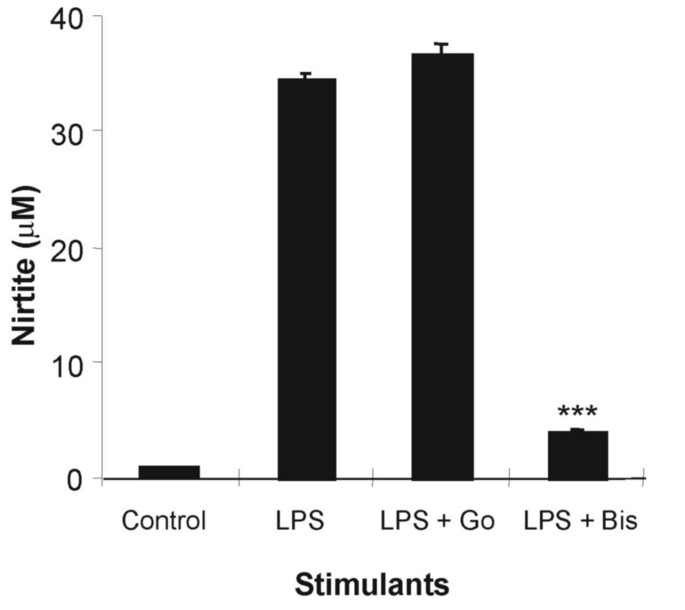
A Novel Class of Antioxidants Inhibit LPS Induction of Tissue Factor by Selective Inhibition of the Activation of ASK1 and MAP Kinases | Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology

Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) concentration in serum(a) and Proteobacteria abundance in faeces of different mouse groups after 14 weeks of dietary intervention (b).

Optimal concentration determination of LPS-conjugates in Arabidopsis... | Download Scientific Diagram

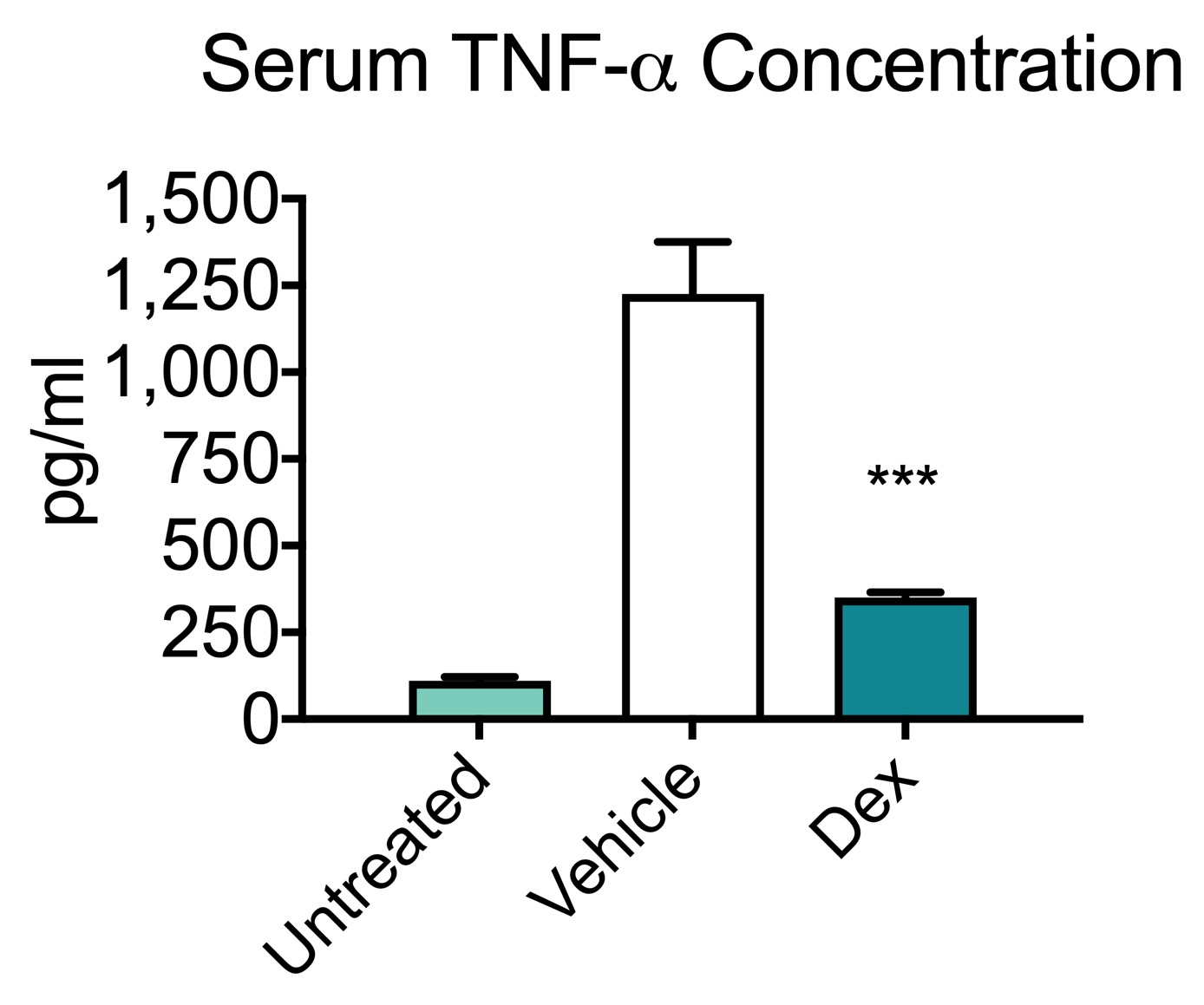
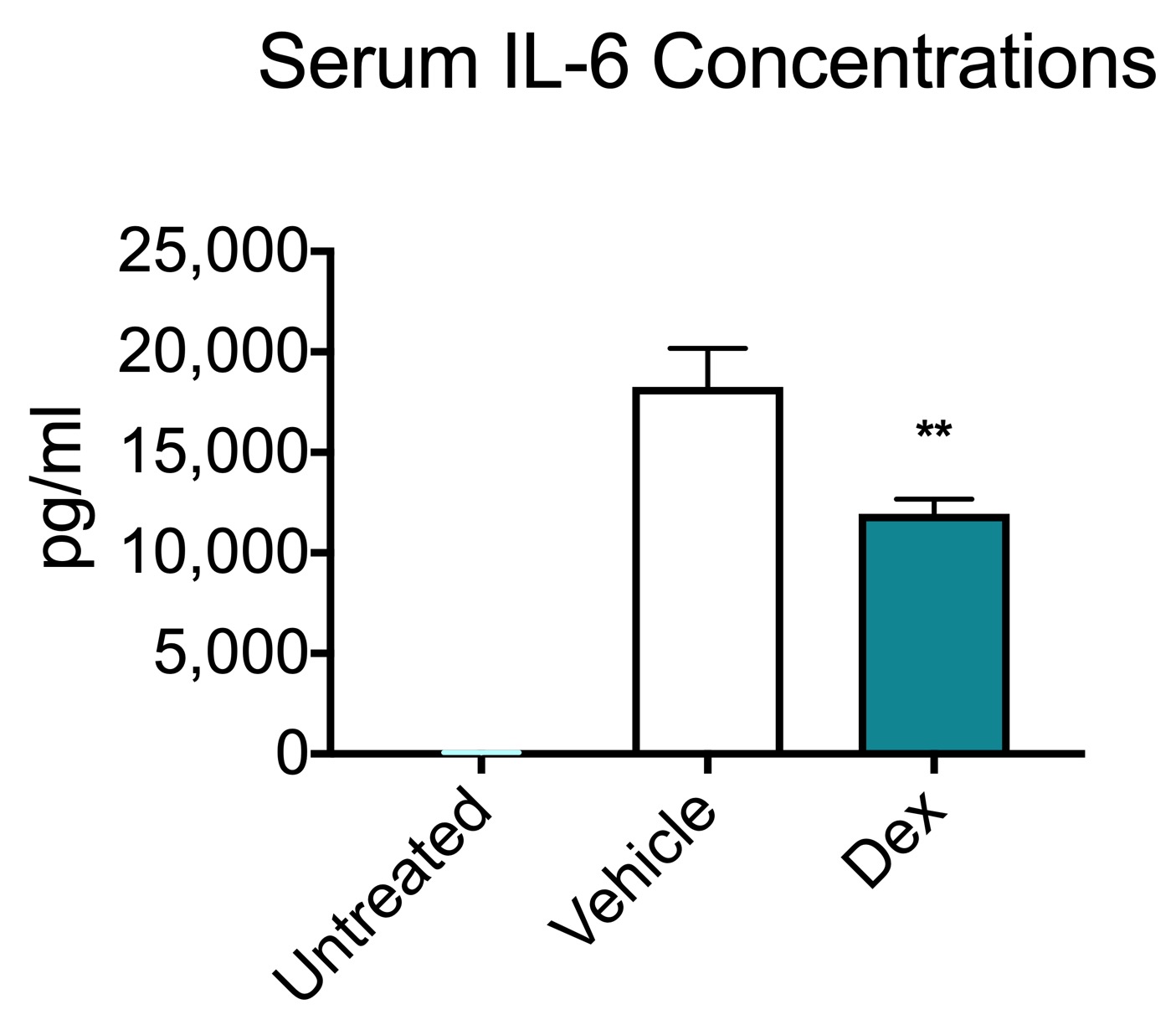
Lipopolysaccharide Causes an Increase in Intestinal Tight Junction Permeability in Vitro and in Vivo by Inducing Enterocyte Membrane Expression and Localization of TLR-4 and CD14 - ScienceDirect

Differential effects of omega-3 fatty acids on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced macrophage activation in combination with cox inhibition - Atherosclerosis

Notch signaling in astrocytes mediates their morphological response to an inflammatory challenge | Cell Death Discovery

Concentration-and time-dependent effects of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) on... | Download Scientific Diagram
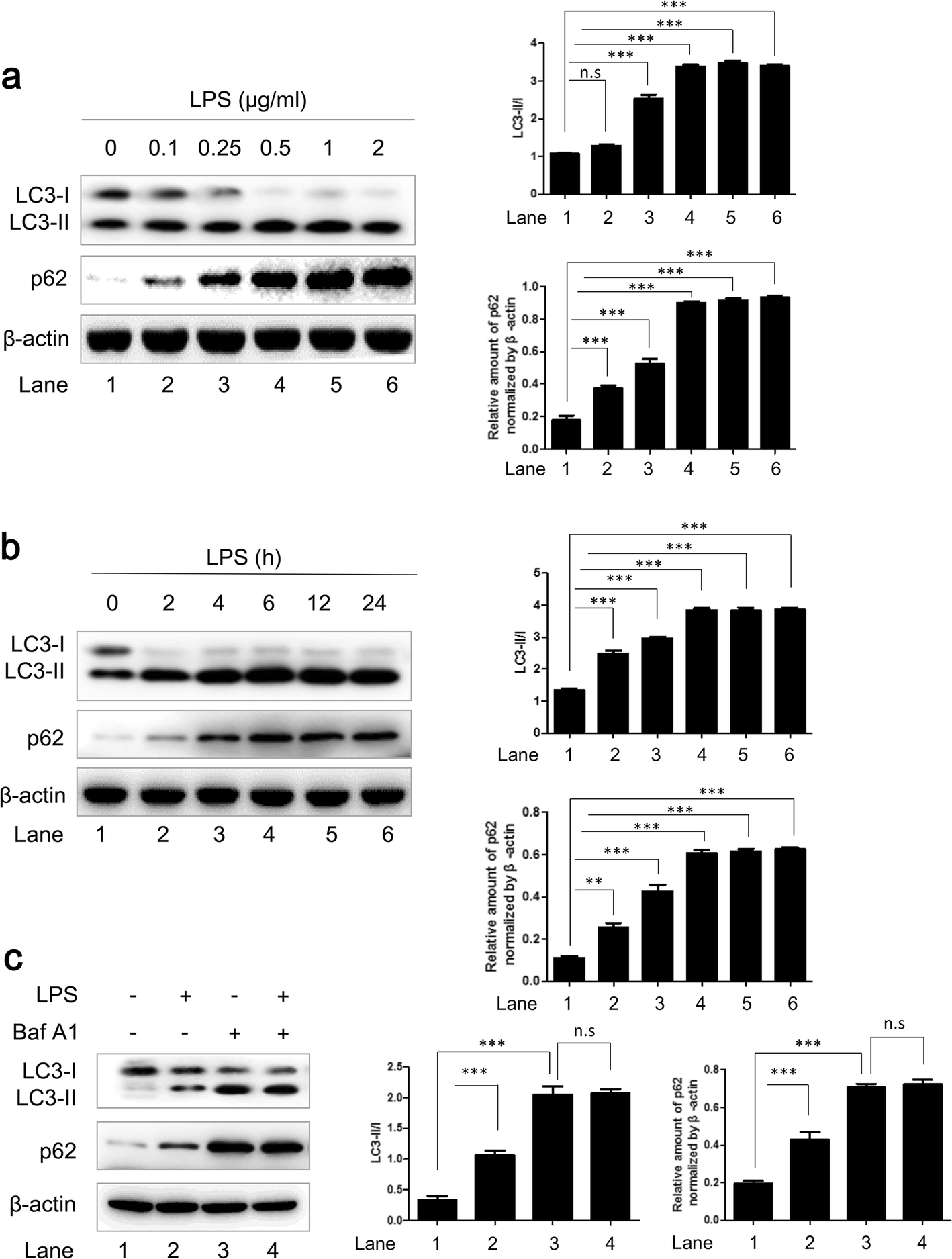
Figure 1 | GSTP1 Inhibits LPS-Induced Inflammatory Response Through Regulating Autophagy in THP-1 Cells | SpringerLink
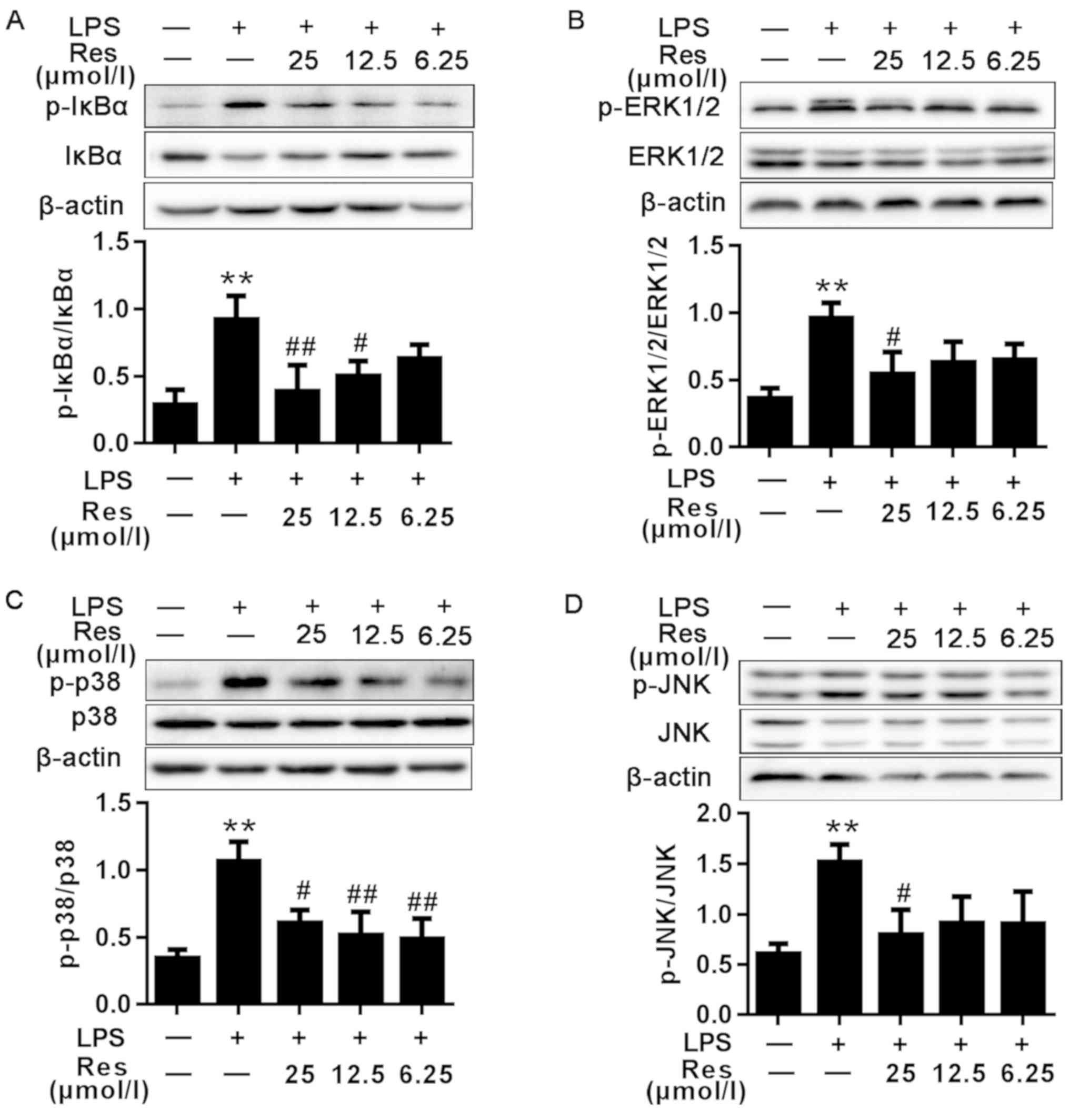
Resveratrol inhibits LPS‑induced inflammation through suppressing the signaling cascades of TLR4‑NF‑κB/MAPKs/IRF3

Naloxone and Ouabain in Ultralow Concentrations Restore Na+/K+-ATPase and Cytoskeleton in Lipopolysaccharide-treated Astrocytes* - Journal of Biological Chemistry

Lipopolysaccharide Causes an Increase in Intestinal Tight Junction Permeability in Vitro and in Vivo by Inducing Enterocyte Membrane Expression and Localization of TLR-4 and CD14 - ScienceDirect
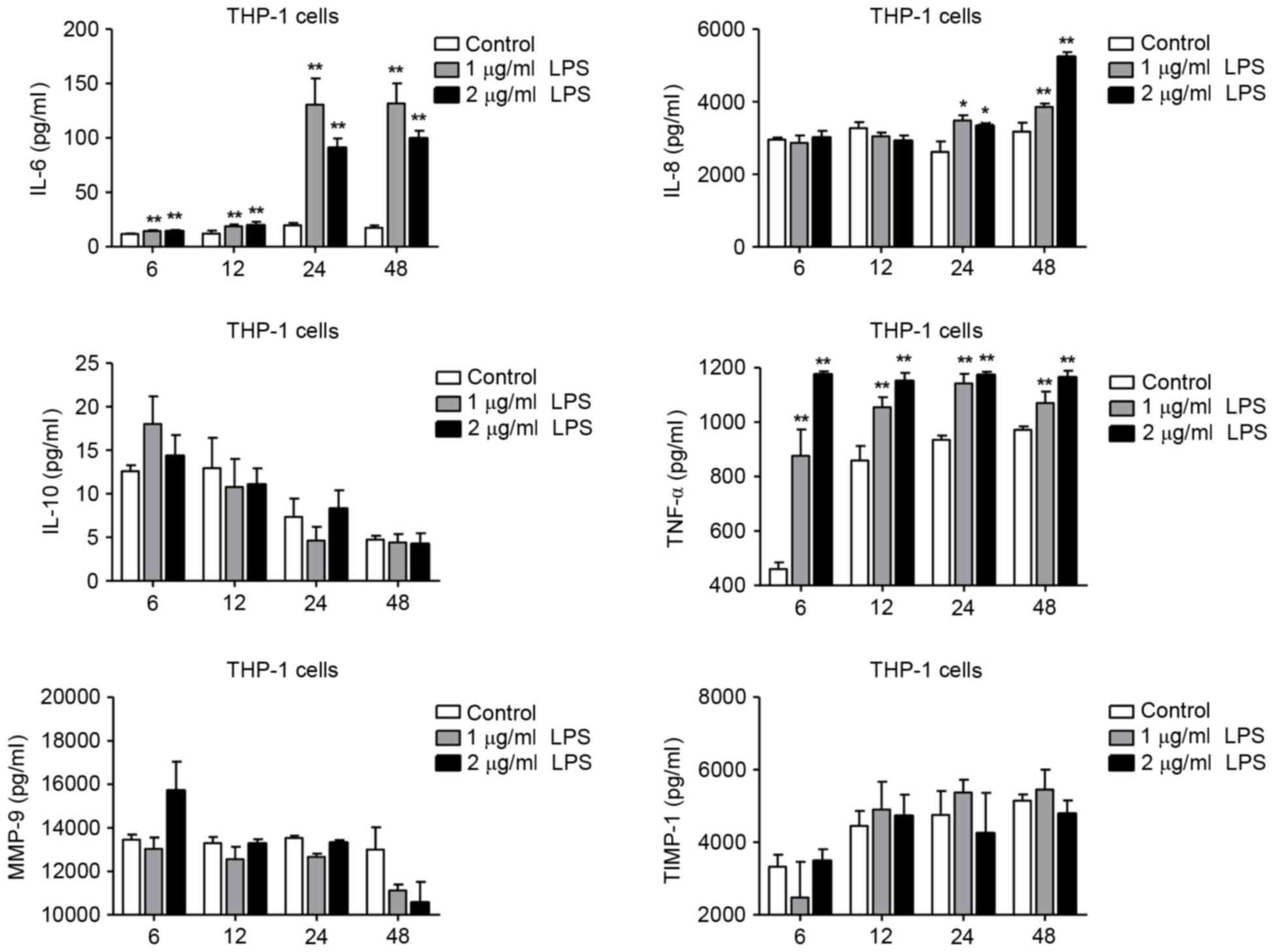
LPS‑induced proinflammatory cytokine expression in human airway epithelial cells and macrophages via NF‑κB, STAT3 or AP‑1 activation
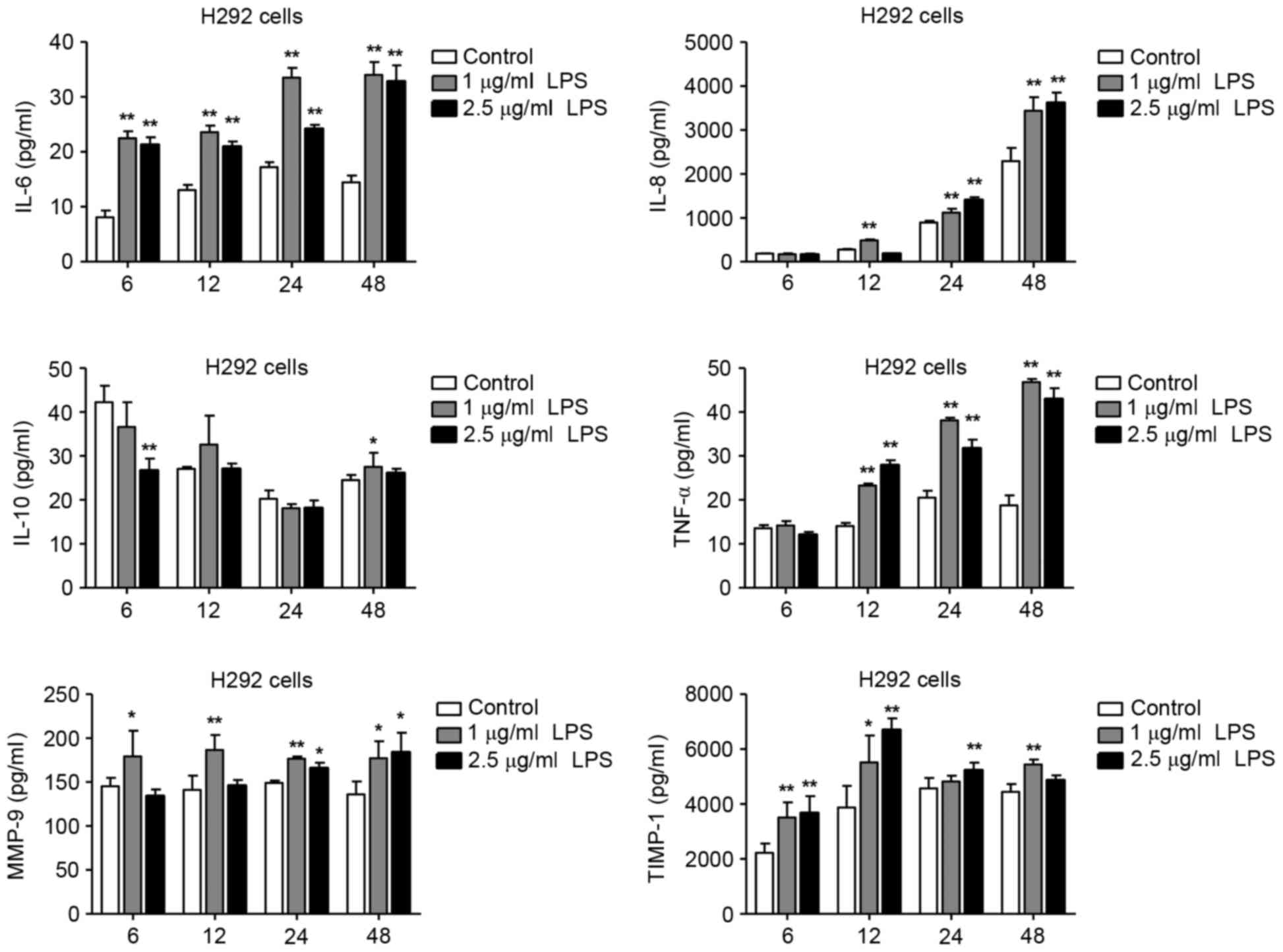
LPS‑induced proinflammatory cytokine expression in human airway epithelial cells and macrophages via NF‑κB, STAT3 or AP‑1 activation

Concentration-and time-dependent effects of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) on... | Download Scientific Diagram

LPS concentration effects on sensitization to DON-induced IL-1b (A, D),... | Download Scientific Diagram

Bacterial endotoxin enhances colorectal cancer cell adhesion and invasion through TLR-4 and NF-κB-dependent activation of the urokinase plasminogen activator system | British Journal of Cancer

M1 Polarization but Anti-LPS-Induced Inflammation and Anti-MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cell Growth Effects of Five Selected Polysaccharides

Pivotal Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in Differential Regulation of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Prostaglandins Production in Macrophages | Molecular Pharmacology